PowerShell Out-File
The Out-File cmdlet in PowerShell sends the output to a specific file. When you need to use its parameters, use this cmdlet instead of redirection operator (>).
Syntax
Parameters
Followings are the parameters used in this cmdlet:
-FilePath and -LiteralPath
Both the parameters are used to specify the path to the file in the command.
-Encoding
This parameter specifies the type of character used in the file. The default value of this parameter is UTF8NoBOM. Followings are the acceptable values for this parameter:
- ASCII
- Unicode
- UTF7
- BigEndianUnicode
- UTF8
- UTF8BOM
- UTF8NoBOM
- OEM
- UTF32
-Append
This parameter is used to add the output at the end of an existing file.
-Force
This parameter overwrites the existing read-only files and the read-only attributes. It does not override security restrictions.
-NoClobber
This parameter prevents the existing files with the same name to be overwritten and shows you a message that the file already exists.
-Width
This parameter specifies the number of characters in each output line.
-NoNewLine
This parameter specifies that the content which is written to the file does not end with a new line character.
-InputObject
This parameter specifies those objects which are written to the file.
-WhatIf
This parameter describes what would happen if the cmdlet executes.
-Confirm
This parameter prompts you a confirmation before executing a cmdlet.
Examples
Example 1:

The command in this example sends the output of the get-childitem cmdlet to the text file whose path is specified in the command by using the -FilePath parameter.
Example 2:
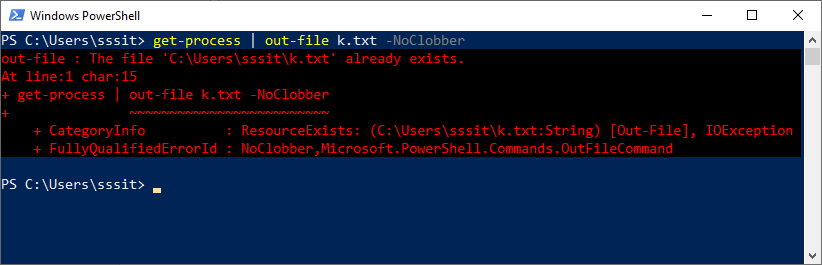
The command in this example does not send the output of the get-process cmdlet to the k.txt file, and it shows an error because the file already exists. The file k.txt cannot be overwritten because of the -NoClobber parameter in the command.





